MIGI 1
Introduction
MIGI 1.1
Purpose of the Guide
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.1.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.2
Structure of the Guide
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 1.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2
Overview of the Handbook
MIGI 2.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2
Content of the Handbook
- 01/12/2004
Where can you find the rules that apply to mortgage and insurance intermediaries?
MIGI 2.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Which parts of the Handbook apply to mortgage and insurance intermediaries?
MIGI 2.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
How are the sourcebooks and manuals structured?
MIGI 2.2.6
See Notes

| Block | Sourcebook or manual | What does it include? | Where in the Guide can I find out more? |
| 1 High Level Standards | PRIN Principles for Businesses | A general statement of the main regulatory obligations of your firm. | Part I, Chapter 3 |
| SYSC Senior Management Arrangements, Systems and Controls | Rules and guidance on how key responsibilities for managing the business should be allocated amongst your senior management team; and the systems and controls your firm should have in place. | Part I, Chapter 3 | |
| COND Threshold Conditions | The minimum standards your firm must satisfy to be authorised by us. | Part I, Chapter 4 | |
| APER Statements of Principles and Code of Practice for Approved Persons | A set of principles and illustrative code of practice that describe the standards of behaviour that we expect of individuals in your firm who are performing 'controlled functions', i.e. functions that have a particular regulatory significance. | Part I, Chapter 6 | |
| FIT The Fit and Proper test for Approved Persons | This sets out the criteria which we use to assess whether an individual is suitable to perform a controlled function. | Part I, Chapter 6 | |
| GEN General provisions | This sets out some of the underlying legal framework to FSA regulation and requirements regarding statutory status disclosure. | Interpreting the Handbook: Part I, Chapter 2.3 Disclosure of status: Part I, Chapter 5 |
| Block | Sourcebook or manual | What does it include? | Where in the Guide can I find out more? |
| 2 Business Standards | PRU Integrated Prudential | The rules about the financial safeguards your firm needs to have in place, for example capital requirements and professional indemnity insurance (PII) requirements. | Capital: Part I, Chapter 7 PII: Part I, Chapter 8 |
| MCOB Mortgages: Conduct of Business | If your firm does mortgage business, these are the requirements relating to how your firm must deal with customers. | Part II, Chapter 2 | |
| ICOB Insurance: Conduct of Business | If your firm does insurance mediation activities, these are the requirements relating to how your firm must deal with customers. | Part III, Chapter 3 | |
| CASS Client Assets | Our requirements on firms that hold client money. These client money rules do not apply to mortgage intermediaries. Insurance intermediaries only have to comply with CASS Chapter 5. The rest of CASS is not covered in the Guide. | Part III, Chapter 2 | |
| TC Training and Competence | The arrangements your firm will need to have in place to ensure staff are appropriately trained and competent for their role. | Mortgage intermediaries: Part II, Chapter 3 Insurance intermediaries: Part III, Chapter 4 |
| Block | Sourcebook or manual | What does it include? | Where in the Guide can I find out more? |
| AUTH Authorisation | Gives guidance to your firm on: whether you need FSA authorisation; the procedures you need to follow for authorisation; and our role in your authorisation. | Part I, Chapter 4 | |
| 3 Regulatory Processes | SUP Supervision | This manual sets out what we do to ensure you are complying with our requirements, including the requirements on what information you need to report to us and when. Chapter 12 of SUP includes the arrangements for firms with appointed representatives |
Variation and cancellation of Permission: Part I, Chapter 16 Reporting and notifications: Part I, Chapter 11 Audit requirements: Part I, Chapter 12 Waivers and rule modifications: Part I, Chapter 17 Appointed representatives: Part I, Chapter 9 Fees: Part I, Chapter 19 |
| DISP Dispute resolution: Complaints | The procedures your firm will need to have in place to handle any complaints made by its customers and the rules that apply to firms subject to the Financial Ombudsman Service. | Part I, Chapter 14 and, on the FOS, Part I, Chapter 18 | |
| 4 Redress | COMP Compensation | Information on the Financial Services Compensation Scheme, which is the scheme to compensate customers if the firm responsible for their loss is not able to pay the claim. | Part 1, Chapter 18 |
- 01/12/2004
Parts of the Handbook not covered in this Guide
MIGI 2.2.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
How do you install the CD-Rom?
MIGI 2.2.11
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2.12
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.2.13
See Notes

| Schedule | Contents |
| 1 | Record keeping requirements (see Part I, Chapter 13 of the Guide) |
| 2 | Notification and reporting requirements (see Part I, Chapter 11 of the |
| Guide) | |
| 3 | Fees (see Part I, Chapter 19 of the Guide) |
| 4 | FSA powers used in making the provisions |
| 5 | Rules where rights of action exist under Section 150 of the Act (action |
| for damages by a person who suffers loss as a result of a breach of the | |
| rules) | |
| 6 | Rules that we have powers to waive or modify (See Part I, Chapter 17 of the Guide) |
- 01/12/2004
How do you install the CD-ROM?
MIGI 2.2.14
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.3
Interpreting the Handbook
- 01/12/2004
What is the difference between rules and guidance?
MIGI 2.3.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.3.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.3.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 2.3.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 3
The Principles and Senior Management
Arrangements, Systems and Controls
MIGI 3.1
Principles for businesses
- 01/12/2004
What are the Principles?
MIGI 3.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 3.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Where are the relevant rules in the Handbook?
MIGI 3.1.3
See Notes

| The Principles | |
| 1 | A firm must conduct its business with integrity. |
| 2 | A firm must conduct its business with due skill, care and diligence. |
| 3 | A firm must take reasonable care to organise and control its affairs responsibly and effectively, with adequate risk management systems. |
| 4 | A firm must maintain adequate financial resources. |
| 5 | A firm must observe proper standards of market conduct. |
| 6 | A firm must pay due regard to the interests of its customers and treat them fairly. |
| 7 | A firm must pay due regard to the information needs of its clients, and communicate information to them in a way, which is clear, fair and not misleading. |
| 8 | A firm must manage conflicts of interests fairly, both between itself and its customers and between a customer and another client. |
| 9 | A firm must take reasonable care to ensure the suitability of its advice and discretionary decisions for any customer who is entitled to rely upon its judgment. |
| 10 | A firm must arrange adequate protection for clients' assets when it is responsible for them. |
| 11 | A firm must deal with its regulators in an open and cooperative way, and must disclose to the FSA appropriately anything relating to the firm of which the FSA would reasonably expect notice. |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 3.2
Senior Management Arrangements, Systems and Controls
- 01/12/2004
What are Senior management arrangements, systems and controls?
MIGI 3.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 3.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 3.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 3.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 3.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 3.2.6
See Notes

| • | Threshold conditions in Authorisation - Part I, Chapter 4 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4
Authorisation
MIGI 4.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.1.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2
The authorisation process
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.1
See Notes

| We: |
| •authorise firms that satisfy the necessary conditions (the threshold conditions) by granting permission to carry on specified regulated activities; |
| •approve individuals to carry on controlled functions in firms as being fit and proper to carry out these functions; |
| •answer technical enquiries about whether firms require authorisation or individuals require approval; |
| •seek to ensure that regulated activities are not being carried out by unauthorised firms; and |
| •collect and maintain intelligence information about authorised firms and individuals so that, for example, we can take action if a firm's authorisation should be removed. |
- 01/12/2004
How do you determine whether your firm requires permission?
MIGI 4.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
The threshold conditions
MIGI 4.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.6
See Notes

| 1. Location of offices | ||
| • | For mortgage intermediaries: | |
| - | If your firm is a body corporate formed in the UK the head office and registered office must be in the UK. | |
| - | If your firm is not a body corporate and has its head office in the UK, it must carry on business in the UK. | |
| • | For insurance intermediaries | |
| - | If your firm is a body corporate formed in the UK the registered office or, if it has no registered office, the head office must be in the UK. | |
| - | If your firm is not a body corporate and has its head office in the UK, it must carry on business in the UK. | |
| 2. Close links | ||
| • | Close links between the firm and other persons must not prevent us from effectively supervising that firm. | |
| 3. Adequate resources | ||
| • | A firm must have adequate resources. | |
| 4. Suitability | ||
| • | The applicant must be fit and proper. | |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What is meant by 'scope of permission'?
MIGI 4.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
The FSA Register
MIGI 4.2.11
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Which parts of the Handbook apply?
MIGI 4.2.12
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.13
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Where can you find further information?
MIGI 4.2.14
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.15
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 4.2.16
See Notes

| • | FSA supervision of small firms - Part I, Chapter 10 |
| • | Approved persons - Part I, Chapter 6 |
| • | Variation and cancellation of permission - Part I, Chapter 16 |
| • | Fees - Part I, Chapter 19 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 5
Disclosure of your Firm's Statutory Status
MIGI 5.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 5.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 5.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 5.2
Statutory status disclosure
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 5.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 5.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 5.2.3
See Notes

| • | Advising and selling standards (MCOB 4) - Part II, Chapter 2.2 |
| • | Advising and selling standards (ICOB 4) - Part III, Chapter 3.3 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6
Approved Persons
MIGI 6.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.2
The approved persons requirements
- 01/12/2004
What are the controlled functions?
MIGI 6.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What are the significant influence functions?
MIGI 6.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
How does the approved persons regime apply to sole traders?
MIGI 6.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Which controlled functions are relevant to small intermediaries?
MIGI 6.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.2.6
See Notes

| Function | Description | Who performs these controlled functions? | What types of firm do these controlled functions apply to? |
| Governing Functions ( SUP 10.6 ) | Individuals responsible for directing the firm's affairs, such as a partner (CF4) or director (CF1) will be performing governing functions. The appropriate governing function will depend on the type of firm. For example, the 'Partner' function would be relevant to a partnership whereas the relevant governing function for a company would be the 'Director' function. |
All of those on the firm's governing body will perform these controlled functions. | Applies to mortgage intermediaries and to primary insurance intermediaries. Does not apply to secondary insurance intermediaries. Unlikely to apply to sole traders |
| Required Functions ( SUP 10.7 ) | The only required function likely to be relevant to smaller insurance and mortgage intermediaries is the 'Apportionment and Oversight Function' (CF8). The person approved to perform this function is responsible for apportioning significant responsibilities among the directors and senior managers and for ensuring that the firm establishes and maintains internal systems and controls that are appropriate for its business. |
If a firm has a chief executive, he or she must be approved to carry on the apportionment and oversight function. Otherwise, in small firms, this controlled function should generally be performed by someone on the firm's governing body. |
Applies to all insurance and mortgage intermediaries. Unlikely to apply to sole traders. |
- 01/12/2004
Might other controlled functions also apply to a mortgage or insurance intermediary?
MIGI 6.2.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.2.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Responsibility for insurance mediation
MIGI 6.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Examples - controlled functions and firm types
MIGI 6.2.11
See Notes

| Type of firm | Relevant Controlled Functions | Points to Note |
| A small partnership that is a mortgage intermediary, a primary insurance intermediary, or both | •CF4 Partner Function (SUP 10.6.17 R) •CF8 Apportionment & Oversight Function (SUP 10.7.1 R) • Allocate responsibility for insurance mediation to one of the above (PRU 9.1.4 R) |
Systems and Control Functions and Significant Management Functions are unlikely to apply. |
| A small company that is a mortgage intermediary, a primary insurance intermediary, or both | •CF1Director Function (SUP 10.6.4 R) CF2 Non Exec Director Function (SUP 10.6.8 R), CF3 Chief Exec Function (SUP 10.6.11 R) •CF8 Apportionment & Oversight Function - (SUP 10.7.1 R) • Allocate responsibility for insurance mediation to one of the above (PRU 9.1.4 R) |
Systems and Control Functions and Significant Management Functions are unlikely to apply. |
| A sole trader that is a mortgage intermediary, an insurance intermediary, or both | • Unlikely to require any approved persons. (SUP 10.6.2 R and SUP 10.6.3 G) • Sole trader will have responsibility for insurance mediation (PRU 9.1.5 G) |
A sole trader only needs to be an approved person him or herself where he or she employs other approved persons |
| A small partnership that is a secondary insurance intermediary only | •CF8 - Apportionment & Oversight Function (SUP 10.7.1 R) • Allocate responsibility for insurance mediation to the above (SUP 10.6.3A G, SUP 10.6.3B G and SUP 10.1.23R (1), SUP 10.1.23R (2)) |
Governing Functions, Systems and Control Functions and Significant Management Functions do not apply. |
| A small company that is a secondary insurance intermediary only | •CF8 - Apportionment & Oversight Function (SUP 10.7.1 R) • Allocate responsibility for insurance mediation to the above (SUP 10.6.3A G,10.6.3B G and 10.7.4A G, 10.7.4B G) |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.3
Approved persons requirements for appointed representatives
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.3.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.3.2
See Notes

will need to be approved persons.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.3.3
See Notes

| Type of AR | Potentially Relevant Controlled Functions |
| A small partnership that is a mortgage mediation AR, a primary insurance mediation AR, or both | •CF4 Partner Function (SUP 10.6.17 R) |
| A small company that is a mortgage mediation AR, a primary insurance mediation AR, or both | •CF1 Director Function (SUP 10.6.4 R) •CF2 Non Exec Director Function (SUP 10.6.8 R) •CF3 Chief Exec Function (SUP 10.6.11 R) |
| A sole trader that is a mortgage mediation AR, a primary insurance mediation AR, or both | • Unlikely to require any approved persons (but see SUP 10.6.2 R and SUP 10.6.3 G) |
| A sole trader that is a secondary insurance mediation AR only | • Unlikely to require any approved persons (but see SUP 10.6.2 R and SUP 10.6.3 G) |
| A small partnership that is a secondary insurance mediation AR only | •CF4 Partner Function (SUP 10.6.17 R) •Only one approved person required |
| A small company that is a secondary insurance mediation AR only | •CF1 Director Function (SUP 10.6.4 R) •CF2 Non Exec Director Function (SUP 10.6.8 R), •CF3 Chief Exec Function (SUP 10.6.11 R) •Only one approved person required |
| An introducer AR introducing mortgage business, insurance business, or both | •Not required to have any approved persons |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.4
Becoming an approved person
- 01/12/2004
What is the test for approval to become an approved person?
MIGI 6.4.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Applying to become an approved person
MIGI 6.4.2
See Notes

Your firm is required to ensure that no-one performs a controlled function until we have granted approval. Applications must be submitted by, or on behalf of, the firm itself, not by the individual who wishes to become an approved person. The principal firm of an AR is responsible for submitting applications for the approval of anyone in the AR who is required to be an approved person.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.4.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.4.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.4.5
See Notes

We must respond to approved persons applications within three months. In practice, the majority of applications are processed much sooner than this.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.5
Principles and Code of Practice for approved persons
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.5.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 6.5.2
See Notes

| • | Authorisation - Part I, Chapter 4 |
| • | Appointed representatives - Part I, Chapter 9 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7
Financial resources requirements
MIGI 7.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.1.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2
The capital resources requirements
- 01/12/2004
What are the capital resources requirements?
MIGI 7.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.5
See Notes

| Type of firm | Capital resources requirement |
| Mortgage intermediary, insurance intermediary, or both, that does not hold client money. | £5,000 or, if higher, 2.5% of the firm's annual income from regulated activities. |
| Mortgage intermediary that holds client money | £10,000 or, if higher, 5% of the firm's annual income from regulated activities. |
| Insurance
intermediary that holds client money in a statutory trust account Insurance intermediary that holds client money relating to transactions with commercial customers in a non-statutory trust account | £10,000 or, if higher, 5% of the firm's annual income from regulated activities. |
| Insurance intermediary that holds client money relating to transactions with retail customers in a non-statutory trust account | £50,000 or, if higher, 5% or the firm's annual income from regulated activities |
- 01/12/2004
What counts towards your firm's annual income?
MIGI 7.2.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What counts towards your firm's capital resources?
MIGI 7.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.11
See Notes

If your firm is a UK-incorporated company, the items eligible for inclusion in its capital resources are:
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.12
See Notes

If your firm is a sole trader, your capital resources are the net balances (according to the sole trader's most recent annual financial statement) on your capital account and current account, plus any eligible subordinated loans.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.13
See Notes

If your firm is a partnership, your capital resources will normally consist of the net balances, (according to the partnership's most recent annual financial statement), on:
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.14
See Notes

If your firm is a limited liability partnership (LLP), your capital resources will normally consist of the net balances (according to the LLP's most recent annual financial statement) on the members' capital account and the members' reserves, plus any eligible subordinated loans.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.15
See Notes

There is a limit on the amount of subordinated loans and redeemable preference shares that your firm may include in its capital resources if it holds client money or client title documents. For details of this restriction, see PRU 9.3.57 R.
- 01/12/2004
Deductions from capital resources
MIGI 7.2.16
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What if my firm has a capital resources or solvency shortfall?
MIGI 7.2.17
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.18
See Notes

| Type of firm | Options in the case of a shortfall |
| A sole trader or a partnership that does not hold client money or client title documents | Personal assets of the sole trader or of a partner may be used to make up the shortfall. This is provided that the personal assets in question are not needed to meet other liabilities arising from the sole trader or partner's personal activities or other business activities not regulated by us. Personal assets may include, for example, a car or a house. |
| A sole trader or a partnership that does hold client money or client title documents | Personal assets may not be used to make up a shortfall. Your firm will need to increase its capital resources. |
| A company, whether or not it holds client money or client title documents | Your firm will need to increase its capital resources. |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.2.19
See Notes

| • | The Principles - Part I, Chapter 3.1 |
| • | Client money - Part III, Chapter 2 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.3
Summary flowchart and worked examples
- 01/12/2004
Summary flowchart: does your firm meet its capital resources requirement?
MIGI 7.3.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.3.2
See Notes

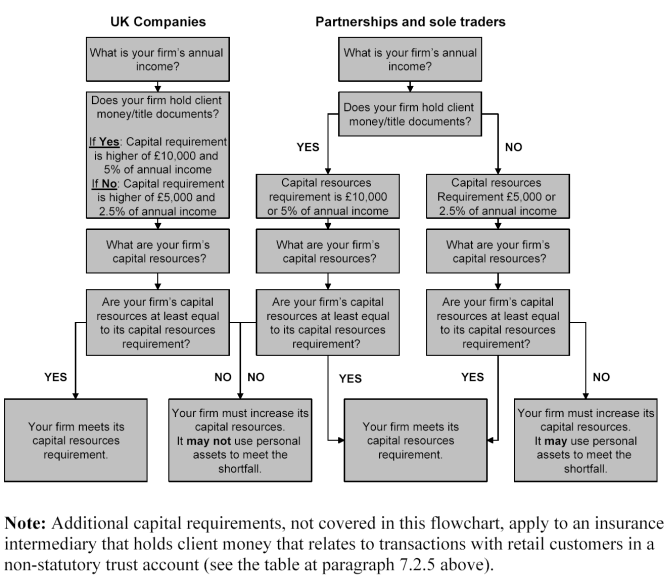
- 01/12/2004
Financial resources requirements: worked examples
MIGI 7.3.3
See Notes

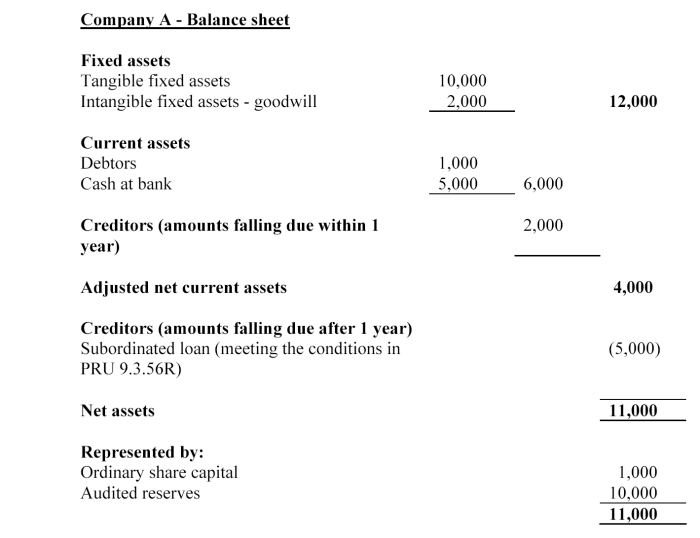
Company A has annual mortgage mediation income of £20,000, according to its last financial statements. Company A does not hold client money.
Company A's capital resources requirement is the higher of £5,000 and 2.5% of its annual mortgage mediation income, i.e. the higher of:
• £5,000; and
• 2.5% of £20,000 = £500
So company A must have capital resources of at least £5,000. Company A's capital resources = share capital + audited reserves + subordinated loan = £1,000 + £10,000 + £5,000 = £16,000.
So Company A meets its capital resources requirement.
Note: from 14 January 2008, Company A must deduct the goodwill on its balance sheet, so from that date, its capital resources will be £14,000, based on this balance sheet and assuming that the subordinated loan has not matured.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.3.4
See Notes

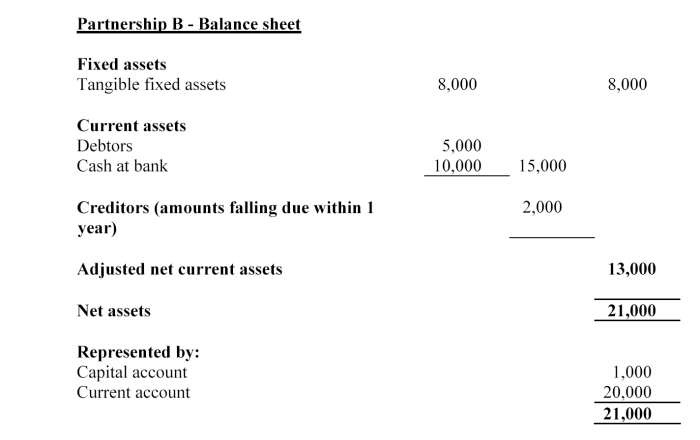
Partnership B, which holds client money in a statutory trust, has annual insurance mediation income of £210,000, according to its last annual financial statement.
Partnership B's capital resources requirement is the higher of £10,000 and 5% of its annual insurance mediation income, i.e. the higher of:
•£10,000; and
• 5% of £210,000 = £10,500.
So Partnership B must have capital resources of at least £10,500.
Partnership B's capital resources = current account + capital account
= £20,000 + £1,000 = £21,000.
So Partnership B meets its capital resources requirement.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 7.3.5
See Notes

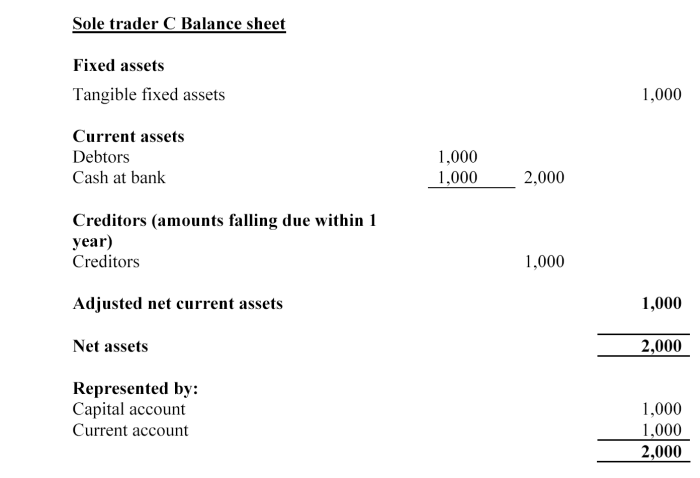
Sole trader C has annual mortgage mediation income of £40,000, according to its last financial statements. Sole trader C does not hold client money. In addition, Sole Trader C has personal assets of £30,000 and personal liabilities of £1,000.
Sole trader C's capital resources requirement is the higher of £5,000 and 2.5% of its annual mortgage mediation income, i.e. the higher of:
•£5,000; and
• 2.5% of £40,000 = £1,000.
So Sole Trader C must have capital resources of at least £5,000.
Sole trader C's capital resources = capital account + current account =
£1,000 + £1,000 = £2,000.
So Sole Trader C has a shortfall of £3,000 in meeting its capital resources requirement.
However, Sole Trader C has net personal assets of £29,000, so £3,000 of these may be used to make up this £2,000 shortfall.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8
Professional indemnity insurance ('PII')
MIGI 8.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.1.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.2
The requirement to hold PII
- 01/12/2004
Which mortgage and insurance intermediaries need to hold PII?
MIGI 8.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3
What must your firm's PII policy cover?
- 01/12/2004
Mortgage mediation: what minimum level of cover must your firm's policy provide?
MIGI 8.3.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Insurance mediation: what minimum level of cover must your firm's policy provide?
MIGI 8.3.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What counts towards your firm's annual income?
MIGI 8.3.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What level of excess should your firm's PII policy have?
MIGI 8.3.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.9
See Notes

| Type of firm | Maximum permitted excess |
| Mortgage intermediary, insurance intermediary, or both that does not hold client money or client title documents | £2,500; or, if higher, 1.5% of annual income. |
| Mortgage intermediary, insurance intermediary, or both that does hold client money or client title documents. | £5,000 or, if higher, 3% of annual income. |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What risks must a PII policy cover?
MIGI 8.3.11
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.12
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.13
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.3.14
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.4
Obtaining PII cover
- 01/12/2004
Who can you get PII cover from?
MIGI 8.4.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
PII policies providing cover for more than one firm
MIGI 8.4.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.4.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.4.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.4.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.5
PII requirements: worked examples
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.5.1
See Notes

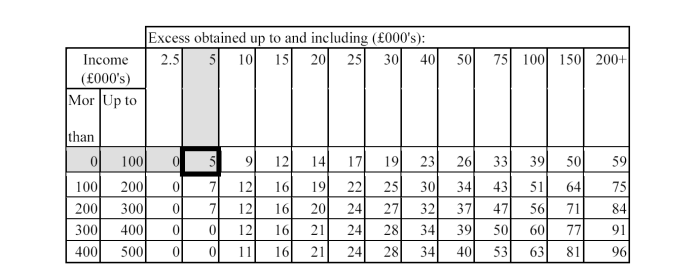
An insurance intermediary that does not hold client money, with annual income of £50,000 receives a quote for a PII policy that has a general excess of £5,000.
Minimum level of cover: €1,000,000 for a single claim AND €1,500,000 for aggregate claims.
The policy contains the following limits: £725,000 for a single claim AND £1,250,000 for aggregate claims.
Assuming an exchange rate of 1.4 when the terms of the policy are agreed, these levels of cover would be sufficient as they convert to €1,015,000 for a single claim and €1,750,000 for aggregate claims.
Excess levels: The maximum permitted excess level is £2,500 (as this is higher than 1.5% of annual income), so the excess on the policy is too high and the policy would not meet our requirements. Using the table in PRU 9.2.21 R shows that the firm would need to hold additional capital of £5,000. The extract from the table below shows how this is calculated.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.5.2
See Notes

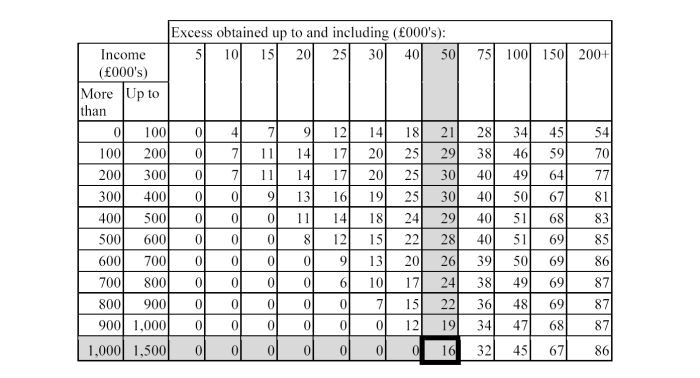
Two unconnected insurance intermediaries, who both hold client money, wish to be covered by the same policy. Firm A has annual income of £1,250,000 and Firm B has annual income of £14,750,000. The policy quote has a general excess of £50,000.
Minimum level of cover required: €1,000,000 for a single claim AND £1,600,000 for aggregate claims. (The policy must cover single claims for €1,000,000 and it must cover aggregate claims for 10% of combined annual income (i.e. £1.6m), as this is greater than €1,500,000 (approx £1,100,000).)
Excess levels: As the £50,000 excess level is less than 3% of the annual income of firm B, the excess is acceptable for firm B. For firm A, the maximum permitted excess level is £37,500 (3% of £1,250,000). So the excess on the policy is too high for firm A and the policy would not meet our requirements. Using the table in PRU 9.2.22 R shows that firm A would need to additional capital of £16,000. The extract from the table below shows how this is calculated.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 8.5.3
See Notes

A mortgage intermediary, that does not handle client money, has annual income of £3,000,000, receives a quote for a PII policy that has a general excess of £2,500.
Minimum level of cover required: £300,000 for a single claim OR £500,000 for aggregate claims (The policy must either cover single claims for 10% of annual income (i.e. £300,000) as this is higher than £100,000 or it must cover aggregate claims for £500,000, as this is higher than 10% of annual income.)
Excess levels: As the £2,500 excess level is less than the maximum permitted (1.5% of £3 million), the firm would not need to hold additional capital.
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9
Appointed representatives
MIGI 9.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2
Appointed representatives
- 01/12/2004
What is an appointed representative?
MIGI 9.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What are a principal's responsibilities?
MIGI 9.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What regulated activities can an AR carry on?
MIGI 9.2.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.7
See Notes

| Regulated activity | General insurance contract | Pure protection contract | Regulated mortgage |
| Arranging | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Advising | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dealing as agent | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| Assisting in the administration and performance | Yes | Yes | N/A |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What if there is more than one principal?
MIGI 9.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.11
See Notes

| Type of AR | Limit on number of principals? |
| AR carrying on mortgage mediation activities in relation to regulated mortgage contracts | Up to two principals - one for standard mortgages and one for lifetime mortgages |
| AR carrying on insurance mediation activities in relation to non-investment insurance contracts | No limits |
| IAR (insurance mediation activities) | No limits |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.12
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Can an AR hold client money?
MIGI 9.2.13
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Does an AR need to have approved persons?
MIGI 9.2.14
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.15
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 9.2.16
See Notes

| Approved Persons - Part I, Chapter 6.3 |
| Statutory status disclosure - Part I, Chapter 5 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10
FSA supervision of small firms
MIGI 10.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.2
Framework
- 01/12/2004
What is the FSA's approach?
MIGI 10.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.2.3
See Notes

| 1. | Maintaining confidence in the financial system; |
| 2. | Promoting public understanding of the financial system; |
| 3. | Securing the appropriate degree of protection for consumers; and |
| 4. | Reducing the extent to which it is possible for a regulated business to be used for a purpose connected with financial crime. |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
How does the FSA monitor small firms?
MIGI 10.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.2.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What is the FSA's supervision strategy for small firms?
MIGI 10.2.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What is the FSA's supervision stategy for small firms?
MIGI 10.2.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 10.2.11
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11
Reporting and Notifications
MIGI 11.1
Reporting requirements
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Why do we require periodic information from firms?
MIGI 11.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
How is information submitted?
MIGI 11.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
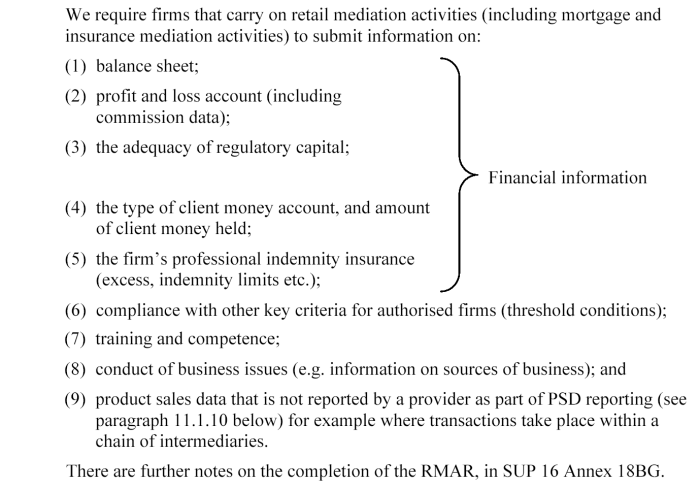
What information do you need to submit in the RMAR?
MIGI 11.1.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
When and how often do I have to submit the RMAR?
MIGI 11.1.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.1.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.1.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.1.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Other reporting requirements
MIGI 11.1.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.1.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.2
Notifications
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Matters having a serious regulatory impact
MIGI 11.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Communications with us in line with Principle 11
MIGI 11.2.3
See Notes

| 1. Any proposed restructuring, reorganisation or business expansion, which could have a significant impact on your firm's risk profile or resources, including but not limited to: | |
| Starting to provide a new product or service (you may need to apply for a variation of permission). | |
| Ceasing to undertake a regulated or ancillary activity, or significantly reducing the scope of such activities. (You may need to apply for a variation of permission). | |
| Entering into, or significantly changing, a material outsourcing arrangement. | |
| Any change in your firm's prudential category. | |
| 2. Any significant failure of your firm's systems or controls (including those reported to your firm by your auditor - if applicable). | |
| 3. Any action that your firm proposes to take which would result in a material change in its capital adequacy or solvency including, but not limited to: | |
| Any action that would result in a material change in your firm's financial resources or financial resources requirement. | |
| A material change resulting from the payment of a special or unusual dividend or the repayment of share capital or a subordinated loan | |
| 4. Significant breaches of rules or other requirements under the Act, e.g. professional indemnity insurance cover being refused or cancelled. | |
- 01/12/2004
Core information where advance notice is required
MIGI 11.2.4
See Notes

| Notification | Supervision sourcebook (SUP) reference |
| A change in your firm's name | SUP 15.5.1 R |
| A change in address (to the principal place of business) | SUP 15.5.4 R |
| A
change to the legal status of your firm (You may be required to send us a new application for Part IV permission.) | SUP 15.5.5 R |
| A change to supervision by an overseas regulator | SUP 15.5.7 R |
- 01/12/2004
General notification requirements
MIGI 11.2.5
See Notes

| Breaches of rules and other requirements in or under the Act | SUP 15.3.11 R |
| Civil, criminal or disciplinary proceedings against a firm | SUP 15.3.15 R |
| Fraud, errors and other irregularities | SUP 15.3.17 R |
| Insolvency, bankruptcy and winding up | SUP 15.3.21 R |
| Change of accounting reference date | SUP 16.3.17 R |
| Change of controller | SUP 11.3 |
| Approved
persons: employees who start performing controlled functions, those who change
or add controlled functions or those who cease performing controlled functions. (There are standard forms to use called 'Approved Persons regime forms' - see Part I, paragraph 6.4.4.) | SUP 10.11 |
| Change of auditor (appointed under FSA rules) | SUP 3.3 |
- 01/12/2004
When should you notify us?
MIGI 11.2.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
How do you notify us?
MIGI 11.2.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.2.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Other considerations
MIGI 11.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 11.2.11
See Notes

| Authorisation - Part I, Chapter 4 |
| Complaints Reporting to the FSA - Part I, Chapter 14.3 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 12
Auditors
MIGI 12.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 12.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 12.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 12.2
FSA and Companies Act 1985 requirements to appoint an auditor
- 01/12/2004
FSA requirements - mortgage intermediaries
MIGI 12.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
FSA requirements - insurance intermediaries
MIGI 12.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 12.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
CA 85 requirements - mortgage and insurance intermediaries
MIGI 12.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Other FSA requirements relating to auditors
MIGI 12.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Summary table
MIGI 12.2.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 12.2.7
See Notes

| AUTHORISED FIRM TYPE | Requirement to appoint auditor under: | FSA auditor rules applicable to: | |||
| Companies Act 1985 | FSA Rules (SUP 3.1) | Firm | Auditor | ||
| Insurance intermediaries | |||||
| Incorporated under CA 85 and: | Para 12.2.3 (above) applies | Yes | Yes | SUP 3.1 - 3.7 | SUP 3.1, SUP 3.2, SUP 3.8, SUP 3.10 |
| Para 12.2.2 (above) applies | Yes | No | SUP 3.1, SUP 3.2, SUP 3.7 | SUP 3.1, SUP 3.2, SUP 3.8 | |
| Not incorporated and: | Para 12.2.3 (above) applies | No | Yes | SUP 3.1 - 3.7 | SUP 3.1, SUP 3.2, SUP 3.8, SUP 3.10 |
| Para 12.2.2 (above) applies | No | No | None | None | |
| Mortgage intermediaries | |||||
| Incorporated under CA 85: | Yes | No | SUP 3.1, SUP 3.2, SUP 3.7 | SUP 3.1, SUP 3.2, SUP 3.8 | |
| Not incorporated (and have no auditor) | No | No | None | None | |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 12.2.8
See Notes

| Client money - Part III, Chapter 2 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 13
Record Keeping
MIGI 13.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 13.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 13.2
General Requirement
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 13.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 13.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 13.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14
Complaints
MIGI 14.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.2
How to handle a complaint
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Where and when should you publicise your procedures?
MIGI 14.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
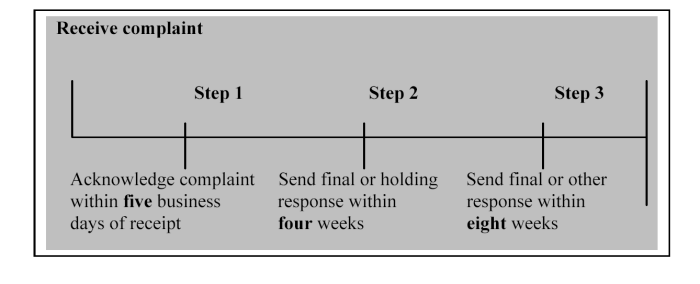
How quickly do you need to deal with a complaint?
MIGI 14.2.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.2.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Where are the relevant Handbook sections?
MIGI 14.2.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Complaints about matters that occurred prior to the commencement of regulation
MIGI 14.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Record keeping requirements
MIGI 14.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.3
Complaints reporting to the FSA
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.3.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
When and how often should I submit complaints reports?
MIGI 14.3.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.3.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
How do I submit a report?
MIGI 14.3.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 14.3.5
See Notes

| Reporting Requirements - Part I, Chapter 11.1 |
| The FCSC and The FOS - Part I, Chapter 18 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 15
Financial Crime
MIGI 15.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 15.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 15.2
Financial Crime
- 01/12/2004
What action does your firm have to take in relation to financial crime?
MIGI 15.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 15.2.2
See Notes

| • | Senior Management Arrangements, Systems and Controls - Part I, Chapter 3.2 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 16
Variation and cancellation of permission
MIGI 16.1
Variation of Permission (VOP)
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 16.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 16.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 16.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 16.1.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 16.1.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 16.2
Cancellation of Permission
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 16.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 17
Waivers and rule modifications
MIGI 17.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 17.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 17.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 17.2
Waivers and rule modifications
- 01/12/2004
What is the FSA's general approach to waivers and rule modifications?
MIGI 17.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 17.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 17.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 17.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What is waiver by consent?
MIGI 17.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 18
The FSCS and the FOS
MIGI 18.1
The Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
- 01/12/2004
What is the FSCS?
MIGI 18.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What is the scope of the FSCS?
MIGI 18.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 18.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 18.1.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What levels of compensation are provided by the FSCS?
MIGI 18.1.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 18.1.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What is the contribution structure of FSCS?
MIGI 18.1.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 18.2
The Financial Ombudsman Scheme (FOS)
- 01/12/2004
What is the FOS?
MIGI 18.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What is the scope of the FOS?
MIGI 18.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 18.2.3
See Notes

The following chapters of this Guide are also relevant:
| Complaints - Part I, Chapter 14 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19
Fees
MIGI 19.1
Introduction
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2
FSA fees
- 01/12/2004
How do FSA fees work?
MIGI 19.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What are application fees?
MIGI 19.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
What are periodic fees?
MIGI 19.2.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.7
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.8
See Notes

Periodic fee = (tariff base data for firm) applied to (fee-block tariff rates)
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Where are the relevant Handbook sections?
MIGI 19.2.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.11
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.12
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 19.2.13
See Notes

| Authorisation - Part I, Chapter 4 |
| Variation of Permission - Part I, Chapter 16.1 |
- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20
Further information
MIGI 20.1
FSA contacts
- 01/12/2004
Handbook and publications
MIGI 20.1.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.1.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.1.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.1.4
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.1.5
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.1.6
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.1.7
See Notes

FSA Events and Conferences: Contact the FSA Events team by phone on 020 7066 0098, by fax on 020 7676 0063 or email at events@fsa.gov.uk
- 01/12/2004
FSA Authorisation and Approved persons
MIGI 20.1.8
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.1.9
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
FSA Fees
MIGI 20.1.10
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Contact Centre
MIGI 20.1.11
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.2
Other contacts
- 01/12/2004
Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS)
MIGI 20.2.1
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI 20.2.2
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)
MIGI 20.2.3
See Notes

- 01/12/2004
MIGI APP 1
Appendix A: brief description of key terms in the Guide
MIGI APP 1.1
Appendix A: brief description of key terms in the Guide
- 01/12/2004
MIGI APP 1.1.1
See Notes

| Defined term | Meaning |
| Appointed representative (AR) | A person or firm that carries on certain regulated activities under the responsibility of a principal. The principal must be an authorised firm and has full responsibility for ensuring that the AR complies with our requirements. |
| Approved person | A person to whom the FSA has given its approval for the performance of a controlled function. |
| Client assets | Assets that you hold on behalf of a client, for example, client money and client title documents such as bearer bonds. |
| Client money | Money that a firm holds on behalf of a client in the course of carrying on mortgage or insurance mediation activities. In the case of insurance mediation activities, this includes money that a firm treats as client money in line with the FSA client money rules set out in CASS. |
| Controlled function | Controlled functions are those jobs or functions within an authorised firm that have a particular regulatory significance, such as being a member of the governing body of the firm. You will find a full list of the controlled functions at SUP 10.4.5 R. |
| Customer | In relation to insurance mediation activities, a 'customer' is, broadly, a policyholder or potential policyholder. This can include a member of a group insurance policy who has direct rights under the policy, e.g. to claim. In relation to mortgage mediation activities, a 'customer' is, broadly, a borrower or potential borrower (who is an individual or trustee). |
| Eligible complainant | A person eligible to have a complaint considered by the Financial Ombudsman Service as defined in DISP 2.4. |
| Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS) | The scheme provided under Part XVI of the Act (the Ombudsman Scheme) under which certain disputes may be resolved quickly and with minimum formality by an independent person. Further details are in DISP. |
| Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) | The scheme set up to pay compensation to customers of FSA authorised firms. It can pay compensation if an FSA authorised firm is unable to pay claims against it, usually because it has gone out of business. Further details are in COMP. |
| The Act | The Financial Services and Markets Act 2000. |
| FSA Register | This is a public record of financial services firms, individuals and other bodies that fall under our regulatory jurisdiction. It can be accessed on our website at www.fsa.gov.uk/register/. |
| General insurance contract | Any contract of insurance within Part 1 Schedule 1 to the Regulated Activities Order (Contracts of General Insurance), for example motor insurance and home contents insurance. |
| Governing body | The board of directors, committee of management or other governing body of a firm. In relation to a sole trader, the sole trader him or herself would be the governing body. |
| The Handbook | The FSA Handbook of Rules and Guidance. |
| Insurance intermediary | A firm carrying on insurance mediation activities. |
| Insurance mediation activity | Any of the following regulated activities: (1) dealing as agent in contracts of insurance; (2) arranging (bringing about) deals in contracts of insurance; (3) making arrangements with a view to transactions in contracts of insurance; (4) assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance; (5) advising on contracts of insurance; and (6) agreeing to carry on any of the above activities. |
| Mortgage intermediary | A firm that arranges regulated mortgages or makes arrangements with a view to regulated mortgages. |
| Mortgage lender | A firm with permission (or which ought to have permission) for entering into a regulated mortgage contract. |
| Mortgage mediation activity | Advising on, arranging or making arrangements with a view to regulated mortgages. |
| Non-investment insurance contract | A contract of insurance that is a general insurance contract or a pure protection contract but which is not a long-term care insurance contract. |
| Permission | Permission given by the FSA under Part IV of the Act to carry on regulated activities. |
| Principles | One of the principles set out in PRIN 2.1.1 R (Principles for Businesses) contained in the Principles for Businesses sourcebook. |
| Pure protection contract | A long-term insurance contract that is not an investment product, e.g. critical illness insurance. |
| Retail Mediation Activities Return (RMAR) | This is the information we propose to require mortgage and insurance intermediaries to submit to us electronically. |
| Regulated activity | Any of the activities specified in Part II of the Regulated Activities Order. |
| Regulated Activities Order | The Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (Regulated Activities) Order 2001. |
- 01/12/2004
