PERG 5
Guidance on insurance mediation activities
PERG 5.1
Application and purpose
- 01/07/2005
Application
PERG 5.1.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Purpose of guidance
PERG 5.1.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.1.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.1.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.1.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.1.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Effect of guidance
PERG 5.1.7
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.1.8
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.1.9
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.1.10
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Guidance on other activities
PERG 5.1.11
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.2
Introduction
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.2.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Requirement for authorisation or exemption
PERG 5.2.2
See Notes

- 01/02/2006
Questions to be considered to decide if authorisation is required
PERG 5.2.3
See Notes

If a person gets as far as question (8) and the answer to that question is "no", that person requires authorisation and should refer to AUTH 3 (Application for Part IV Permission) The order of these questions considers firstly whether a person is carrying on insurance mediation activities before dealing separately with the questions "will I be carrying on my activities by way of business?" (3) and "if so, will any or all of my activities by excluded?" (5).
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.2.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Approach to implementation of the IMD
PERG 5.2.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.2.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.2.7
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.2.8
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.2.9
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Financial promotion
PERG 5.2.10
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.3
Contracts of insurance
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.3.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Definition
PERG 5.3.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.3.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.3.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.3.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.3.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Connected contracts of insurance
PERG 5.3.7
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Large risks
PERG 5.3.8
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Specified investments
PERG 5.3.9
See Notes

'Relevant investments' is the term used in articles 21 (Dealing in investments as agent), 25 (Arranging deals in investments) and 53 (Advising on investments) of the Regulated Activities Order to help define the types of investment to which the activities in each of these articles relate.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.3.10
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.3.11
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4
The business test
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4.7
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.4.8
See Notes

| Carrying on insurance mediation activities 'for remuneration' and 'by way of business' | ||
| 'For remuneration' | ||
| Factor | Indicators that P does not carry on activities "for remuneration" | Indicators that P does carry on activities "for remuneration" |
Direct remuneration, whether received from the customer or the insurer/broker (cash or benefits in kind such as tickets to the opera, a reduction in other insurance premiums, a remission of a debt or any other benefit capable of being measured in money's worth) | P does not receive any direct remuneration specifically identified as a reward for his carrying on insurance mediation activities. | P receives direct remuneration specifically identified as being a reward for his carrying on insurance mediation activities. |
| Indirect remuneration (such as any form of economic benefit as may be explicitly or implicitly agreed between P and the insurer/broker or P's customer - including, for example, through the acceptance of P's terms and conditions or mutual recognition of the economic benefit that is likely to accrue to P). An indirect economic benefit can include expectation of making a profit of some kind as a result of carrying on insurance mediation activities as part of other services. | P does not obtain any form of indirect remuneration through an economic benefit other than one which is not likely to have a material effect on P's ability to make a profit from his other activities. | P obtains an economic benefit that: (a) is explicitly or implicitly agreed between P and the insurer/broker or P's customer; and (b) has the potential to go beyond mere cost recovery through fees or other benefits received for providing a package of services that includes insurance mediation activities but where no particular part of the fees is attributable to insurance mediation activities. This could include where insurance mediation activities are likely to: •play a material part in the success of P's other business activities or in P's ability to make a profit from them; or•provide P with a materially increased opportunity to provide other goods or services; or•be a major selling point for P's other business activities; or•be essential for P to provide other goods or services. P charges his customers a greater amount for other goods or services than would be the case if P were not also carrying on insurance mediation activities for those customers and this: •is explicitly or implicitly agreed between P and the insurer/broker or P's customer; and•has the potential to go beyond mere cost recovery. |
| Recovery of costs | P receives no benefits of any kind (direct or indirect) in respect of his insurance mediation activities beyond the reimbursement of his actual costs incurred in carrying on the activity (including receipt by P of a sum equal to the insurance premium that P is to pass on to the insurer or broker). | P receives benefits of any kind (direct or indirect) in respect of his insurance mediation activities which go beyond the reimbursement of his actual costs incurred in carrying on the activity. |
| 'By way of business' | ||
| Factor | Indicators that P does not carry on activities "by way of business" | Indicators that P does carry on activities "by way of business" |
| Regularity/ frequency | Involvement is one-off or infrequent (for instance, once or twice a year) provided that the transaction(s) is not of such size and importance that it is essential to the success of P's other business activities. Transactions do not result from formal arrangements (for instance, occasional involvement purely as a result of an unsolicited approach). | Involvement is frequent (for instance, once a week). Involvement is infrequent but the transactions are of such size or importance that they are essential to the success of P's other business activities. P has formal arrangements which envisage transactions taking place on a regular basis over time (whether or not such transactions turn out in practice to be regular). |
| Holding out | P does not hold himself out as providing a professional service that includes insurance mediation activities (by professional is meant not the services of a layman). | P holds himself out as providing a professional service that includes insurance mediation activities. |
| Relevance to other activities/ business |
Insurance mediation activities: •have no relevance to P's other activities; or•have some relevance but could easily be ceased without causing P any difficulty in carrying on his main activities; or•would be unlikely to result in a material reduction in income from P's main activities if ceased |
Insurance mediation activities: •are essential to P in carrying on his main activities; or•would cause a material disruption to P carrying on his main activities if ceased; or•would be likely to reduce P's income by a material amount. |
| Commercial benefit | P receives no direct or indirect pecuniary or economic benefit. P is a layman and acting in that capacity. P would not obtain materially less income from his main activities if they did not include insurance mediation activities. | P receives a direct or indirect pecuniary or economic benefit from carrying on insurance mediation activities - such as a fee, a benefit in kind or the likelihood of materially enhanced sales of other goods or services that P provides. P would obtain materially less income from his main activities if they did not include insurance mediation activities. |
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.5
The regulated activities: dealing in contracts as agent
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.5.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.5.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.5.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6
The regulated activities: arranging deals in, and making arrangements with a view to transactions in, contracts of insurance
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Article 25(1): arranging (bringing about) deals in investments
PERG 5.6.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Article 25(2): making arrangements with a view to transactions in investments
PERG 5.6.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Exclusion: article 72C (Provision of information on an incidental basis)
PERG 5.6.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.7
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.8
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.9
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Exclusion from article 25(2): arrangements enabling parties to communicate
PERG 5.6.10
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.11
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Exclusion from article 25(2): transactions to which the arranger is a party
PERG 5.6.12
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.13
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.14
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.15
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.16
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Exclusion from article 25(2) for introducing
PERG 5.6.17
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.18
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.19
See Notes

This is because the arrangements for making introductions do not specifically relate to a contract of insurance or to any other type of investment but to investments generally. Whether or not a person is making arrangements for introductions for the purpose of the provision of independent advice on investments generally will depend on the facts in any particular case. But, in the FSA's view, it is very unlikely that article 33 could apply where introductions are made to a person for the purposes of that person giving advice on and then arranginggeneral insurance.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.20
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.6.21
See Notes

| Type of introduction | Applicability of exclusion | |
| 1 | Introductions are purely for the purpose of the provision of independent advice - Introducer is completely indifferent to whether or not transactions take place after advice has been given. | Exclusion not relevant as introducer is not arranging under article 25(2). |
| 2 | Introduction is one-off or otherwise not part of pre-existing ongoing arrangements that envisage such introduction being made. | Exclusion not relevant as introducer is not arranging under article 25(2). |
| 3 | Introducer is not indifferent to whether or not transactions take place after advice has been given, but is indifferent to whether or not the transactions may involve a contract of insurance. | Exclusion will be available provided the introduction was made with a view to the provision of independent advice on investments generally. |
4 | Introducer is not indifferent to whether or not transactions take place after advice has been given (for example, because he expects to receive a percentage of the commission), and introductions specifically relate to contracts of insurance. | Exclusion is not available. If introducer is an unauthorised person, he will need authorisation or exemption as an appointed representative. If introducer is an authorised person (such as an IFA introducing to a general insurance broker), he will need to vary his Part IV permission accordingly. If introducer is an appointed representative, he will need to ensure that his agreement covers making such arrangements. |
- 01/07/2005
Exclusion from article 25(2): arrangements for the provision of finance
PERG 5.6.22
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Other exclusions
PERG 5.6.23
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.7
The regulated activities: assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.7.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.7.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.7.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.7.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.7.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.7.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Exclusions
PERG 5.7.7
See Notes

are also excluded from the regulated activity of assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance. This is where the activity is carried on in the course of carrying on any profession or business (see also PERG 5.14 (Exemptions)). In determining whether they are carrying on the regulated activity of assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance, therefore, persons should consider whether they are acting on behalf of the relevant insurer and not the policyholder.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.7.8
See Notes

So, a person whose activities are excluded under article 12 of the Regulated Activities Order (Breakdown insurance) will not be a relevant insurer for these purposes and any person who performs loss adjusting or claims management on behalf of such a person will not be able to use the exclusion in article 39B.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8
The regulated activities: advising on contracts of insurance
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Advice must relate to a particular contract of insurance
PERG 5.8.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.5
See Notes

| Recommendation | Regulated under article 53 or not? |
| I recommend you take the ABC Insurers motor insurance policy | Yes |
| I recommend that you take out the GHI Insurers life insurance policy | Yes |
| I recommend that you do not take out the ABC Insurers motor insurance policy | Yes |
| I recommend that you do not take out the GHI Insurers life insurance policy | Yes |
| I recommend that you take out either the ABC Insurers motor insurance policy or the DEF Insurers motor insurance policy | Yes |
| I recommend that you take out either the GHI Insurers life insurance policy or the JKL Insurers life insurance policy | Yes |
| I recommend that you take out (or do not take out) insurance with ABC Insurers | Possibly (depending on whether or not the circumstances relating to the recommendation, including the range of possible products, is such that this amounts to an implied recommendation of a particular policy) |
| I recommend that you take out (or do not take out) contents insurance | No, unless a specific insurance policy is implied by the context |
| I recommend that you take out (or do not take out) life insurance | No, unless a specific insurance policy is implied by the context |
- 01/07/2005
Advice given to a person in his capacity as an investor or potential investor
PERG 5.8.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.7
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Advice or information
PERG 5.8.8
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.9
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.10
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.11
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Advice must relate to the merits (of buying or selling a contract of insurance)
PERG 5.8.12
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.13
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.14
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Pre-purchase questioning (including decision trees)
PERG 5.8.15
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.16
See Notes

Whether or not pre-purchase questioning in any particular case is advising on contracts of insurance will depend on all the circumstances. The process may involve identifying one or more particular contracts of insurance. If so, to avoid advising on contracts of insurance, the critical factor is likely to be whether the process is limited to, and likely to be perceived by the person as, assisting the person to make his own choice of product which has particular features which the person regards as important. The questioner will need to avoid providing any judgement on the suitability of one or more products for that person and in this respect should have regard to the factors set out in PERG 5.8.2 G to PERG 5.8.4 G (Advice must relate to a particular contract of insurance) and the table in PERG 5.8.5 G. See also PERG 5.8.12 G to PERG 5.8.14 G (Advice must relate to the merits (of buying or selling a contract of insurance)) for other matters that may be relevant.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.17
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.18
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.19
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Medium used to give advice
PERG 5.8.20
See Notes

the use of the medium itself to give advice should make no material difference to whether or not the advice is caught by article 53.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.21
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.22
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.23
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Exclusion: periodical publications, broadcasts and web-sites
PERG 5.8.24
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.8.25
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Other exclusions
PERG 5.8.26
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.9
The Regulated Activities: agreeing to carry on a regulated activity
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.9.1
See Notes

agreeing to do any of these things is itself a regulated activity. In the FSA's opinion, this activity concerns the entering into of a legally binding agreement to provide the services to which the agreement relates. So, a person is not carrying on a regulated activity under article 64 merely because he makes an offer to do so.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.9.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.10
Renewals
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.10.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11
Other aspects of exclusions
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Exclusions disapplied where activities relate to contracts of insurance
PERG 5.11.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.5
See Notes

- 01/01/2007
PERG 5.11.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Exclusions disapplied in connection with insurance mediation
PERG 5.11.7
See Notes

- 01/10/2005
Exclusions applying to more than one regulated activity
PERG 5.11.8
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Activities carried on in the course of a profession or non-investment business
PERG 5.11.9
See Notes

Article 67 excludes from the activities of dealing as agent, arranging (bringing about) deals in investments, making arrangements with a view to transactions in investments, assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance and advising on investments, any activity which:
- (1) is carried on in the course of carrying on any profession or business which does not otherwise consist of the carrying on of regulated activities in the United Kingdom; and
- (2) may reasonably be regarded as a necessary part of other services provided in the course of that profession or business.
In the FSA's view, the fact that a person may carry on regulated activities in the course of the carrying on of a profession or business does not, of itself, mean that the profession or business consists of regulated activities. This is provided that the main focus of the profession or business does not involve regulated activities and that the regulated activities that are carried on arise in a way that is incidental and complementary to the carrying on of the profession or business.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.10
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.11
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.12
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Activities carried on by a provider of relevant goods or services
PERG 5.11.13
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.14
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.11.15
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Large risks
PERG 5.11.16
See Notes

For a fuller definition of contracts of large risks see the definition in the Glossary.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12
Link between activities and the United Kingdom
- 01/07/2005
Introduction
PERG 5.12.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.4
See Notes

| Needs Part IVpermission | Schedule 3 EEA passport rights available | Overseas persons exclusion available | |
| Registered EEA-based intermediary with UK branch (registered office or head office in another EEA State) | No | Yes | No |
| Registered EEA-based intermediary with no UK branch providing cross-border services | No | Yes | Potentially available [see Note] |
| Third country intermediary operating from branch in the UK | Yes | No | No |
| Third country intermediary providing services in (or into) the UK | Yes unless overseas persons exclusion applies | No | Potentially available |
| This does not, however, affect the firm'sauthorisation under Schedule 3 to the Act (see PERG 5.12.9 G to PERG 5.12.10 G (Passporting)). | |||
- 01/07/2005
Where are insurance mediation activities carried on?
PERG 5.12.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.7
See Notes

In each of these cases it is irrelevant where the person with whom the activity is carried on is situated.
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.8
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Overseas persons
PERG 5.12.9
See Notes

A 'legitimate approach', for the purposes of (2), is one that results from an unsolicited approach by a person (for example, a customer) or otherwise is a result of an approach by, or on behalf of, an overseas person which complies with the restriction on financial promotion under section 21 of the Act (see PERG 8.3.1 G (Financial promotion)).
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.10
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
How should persons be authorised?
PERG 5.12.11
See Notes

The United Kingdom will, in each case, be the Home State for the purposes of the IMD for insurance or reinsurance intermediaries (see further in connection with the E-Commerce Directive in PERG 5.12.15 G to PERG 5.12.17 G (E-Commerce Directive)).
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.12
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Passporting
PERG 5.12.13
See Notes

Registered EEA-based insurance intermediaries wishing to establish branches in the United Kingdom or provide services on a cross-border basis into the United Kingdom can do so by notifying their Home State regulator which in turn notifies the FSA . This enables the intermediary to acquire passporting rights under Schedule 3 to the Act (EEA passporting rights) (see Schedule 3(13) and (14) of the Act as amended by the Insurance Mediation Directive (Miscellaneous Amendments) Regulations 2003). SUP 13A (Qualifying for authorisation under the Act) has general guidance on the exercise of passporting rights by EEA firms.
- 01/02/2006
PERG 5.12.14
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
E-Commerce Directive
PERG 5.12.15
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.16
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.12.17
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.13
Appointed representatives
- 01/07/2005
What is an appointed representative?
PERG 5.13.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.13.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Business for which an appointed representative is exempt
PERG 5.13.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.13.4
See Notes

| Type of contract of insurance | Regulated activities an appointed representative can carry on |
| General insurance contract |
•
dealing in investments as agent;•
arranging;•
assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance;•
advising on investments; and•agreeing to carry on these regulated activities.
|
| Pure protection contract |
•
dealing in investments as agent (but only where the contract is not a long-term care insurance contract);•
arranging;•
assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance;•
advising on investments; and•agreeing to carry on these regulated activities.
|
| Life policy |
•
arranging;•
assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance;•
advising on investments; and•agreeing to carry on these regulated activities
|
- 01/07/2005
Persons who are not already appointed representatives
PERG 5.13.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Persons who are already appointed representatives
PERG 5.13.6
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.14
Exemptions
- 01/07/2005
Professionals
PERG 5.14.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.14.2
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.14.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.14.4
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
Other exemptions
PERG 5.14.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15
Illustrative tables
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15.2
See Notes

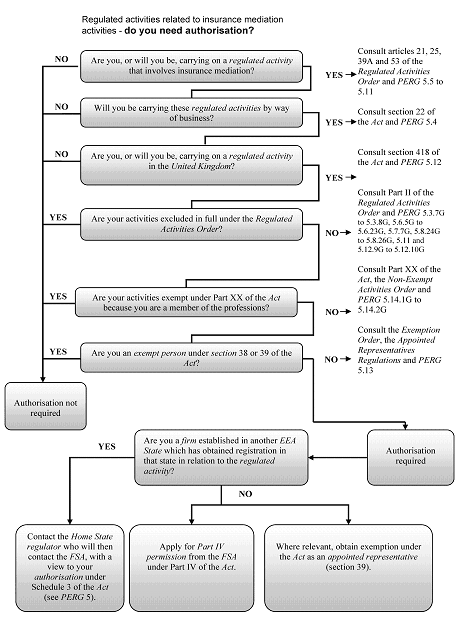
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15.3
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15.4
See Notes

| Type of activity | Is it a regulated activity? | Rationale |
| MARKETING AND EFFECTING INTRODUCTIONS | ||
| Passive display of information -for example, medical insurance brochures in doctor's surgery (whether or not remuneration is received for this activity) | No. | Merely displaying information does not constitute making arrangements under article 25(2) (see PERG 5.6.4 G). |
| Recommending a broker/insurance undertaking and providing customer with contact details (whether by phone, fax, e-mail, face-to-face or any other means of communication) | Yes, but article 72C may be available. | This will constitute making arrangements under article 25(2). But, the exclusion in article 72C will apply if all the intermediary does is supply information to the customer and the conditions of article 72C are otherwise met (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G). Generally, this will not amount to advice under article 53 unless there is an implied recommendation of a particular policy (see PERG 5.8.4 G), in which case article 72C would not be available. |
| Providing an insurance undertaking/broker with contact details of customer | Yes. | This will constitute making arrangements under article 25(2) when undertaken in the context of regular or ongoing arrangements for introducing customers. Article 72C will not apply because the information is supplied to someone other than the policyholder or potential policyholder. |
| Marketing on behalf of insurance undertaking to intermediaries only (for example, broker consultants) | Yes. | This amounts to work preparatory to the conclusion of contracts of insurance and so constitutes making arrangements under article 25(2). Article 72C is not available because this activity does not involve provision of information to the policyholder or potential policyholder only. |
| Telemarketing services (that is, companies specialising in marketing an insurance undertaking's products/services to prospective customers) | Yes. | This amounts to introducing and/or other work preparatory to the conclusion of contracts of insurance and so constitutes making arrangements under article 25(2). This could also involve article 25(1) arranging where the telemarketing company actually sells a particular policy and could involve advising on investments. Article 72C will not be available where the provision of information is more than incidental to the telemarketing company's main business or where the telemarketing company is advising on investments. |
| PRE-PURCHASE DISCUSSIONS WITH CUSTOMERS AND ADVICE | ||
| Discussion with client about need for insurance generally/need to take out a particular type of insurance | Generally, no. Article 72C available if needed. | Not enough, of itself, to constitute making arrangements under article 25(2), but you should consider whether, viewed as a whole, your activities might amount to arranging. If so, article 72C might be of application (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G). |
| Advising on the level of cover needed | Generally, no. Article 72C available if needed. | Not enough, of itself, to constitute making arrangements under article 25(2), but you should consider whether, viewed as a whole, your activities might amount to making arrangements under article 25(2) (see PERG 5.8.3 G). If so, article 72C might be of application (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G). |
| Pre-purchase questioning in the context of filtered sales (intermediary asks a series of questions and then suggests several policies which suit the answers given) | Yes. Subject to article 72 C exclusion where available. | This will constitute arranging although article 72C may be of application (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G). If there is no express or implied recommendation of a particular policy, this activity will not amount to advice under article 53 (see PERG 5.8.15 G to PERG 5.8.19 G). |
| Explanation of the terms of a particular policy or comparison of the terms of different policies | Possibly. Article 72C available. | This is likely to amount to making arrangements under article 25(2). In certain circumstances, it could involve advising on investments (see PERG 5.8.8 G (Advice or information)). Where the explanation is provided to the potential policyholder, and does not involve advising on investments, article 72C may be of application (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G), and where information is provided by a professional in the course of a profession, article 67 may apply (see PERG 5.11.9 G to PERG 5.11.12 G). |
| Advising that a customer take out a particular policy | Yes. | This amounts to advice on the merits of a particular policy under article 53 (see PERG 5.8.4 G to PERG 5.8.5 G). |
| Advising that a customer does not take out a particular policy | Yes. | This amounts to advice on the merits of a particular policy under article 53 (see PERG 5.8.4 G to PERG 5.8.5 G). |
| Advice by journalists in newspapers, broadcasts etc. | Generally, no because of the article 54 exclusion. | Article 54 provides an exclusion for advice given in newspapers etc (see PERG 5.8.24 G to PERG 5.8.25 G). |
| Giving advice to a customer in relation to his buying a consumer product, where insurance is a compulsory secondary purchase and/or a benefit that comes with buying the product | Not necessarily but depends on the circumstances. | Where the advice relates specifically to the merits of the consumer product, it is possible that references to the accompanying insurance may be seen to be information and not advice. If, however, the advice relates, in part, to the merits of the insurance element, then it will be regulated activity. |
| ASSISTING CUSTOMERS WITH COMPLETING/SENDING APPLICATION FORMS | ||
| Providing information to customer who fills in application form | Possibly. Subject to article 67 or 72C exclusions where available. | This activity may amount to arranging although the exclusions in article 67 (see PERG 5.11.9 G to PERG 5.11.12 G) and article 72C (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G) may be of application. |
| Helping a potential policyholder fill in an application form | Yes. | This activity amounts to arranging. Article 72C will not apply because this activity goes beyond the mere provision of information to a policyholder or potential policyholder (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G). |
| Receiving completed proposal forms for checking and forwarding to an insurance undertaking (for example, an administration outsourcing service provider that receives and processes proposal forms) | Yes. | This amounts to arranging. Article 72C does not apply because this activity goes beyond the mere provision of information to a policyholder or potential policyholder (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G). |
| Assisting in completion of proposal form and sending to insurance undertaking | Yes. | This activity amounts to arranging. Article 72C does not apply because this activity goes beyond the mere provision of information (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G). |
| NEGOTIATING AND CONCLUDING CONTRACTS OF INSURANCE | ||
| Negotiating terms of policy on behalf of a customer with the insurance undertaking | Yes. | This activity amounts to arranging (see PERG 5.6.2 G). |
| Negotiating terms of policy on behalf of insurance undertaking with the customer and signing proposal form on his behalf | Yes. | These activities amount to both arranging and dealing in investments as agent. |
| Concluding a contract of insurance on insurance company's behalf, for example, motor dealer who has authority to conclude insurance contract on behalf of insurance undertaking when selling a car | Yes. | A person carrying on this activity will be dealing in investments as agent. He will also be arranging (as the article 28 exclusion only applies in the limited circumstances envisaged under article 28(3)) (see PERG 5.6.12 G). |
| Agreeing, on behalf of a prospective policyholder, to buy a policy. | Yes. | A person who, with authority, enters into a contract of insurance on behalf of another is dealing in investments as agent under article 21, and will also be arranging. |
| Providing compulsory insurance as a secondary purchase | Yes. It will amount to dealing in investments as agent or arranging. | The fact that the insurance is secondary to the primary product does not alter the fact that arranging the package involves arranging the insurance. |
| COLLECTION OF PREMIUMS | ||
| Collection of cheque for premium from the customer at the pre-contract stage. | Yes (as part of arranging). | This activity is likely to form part of arranging. But the mere collection/receipt of premiums from the customer is unlikely, without more, to amount to arranging. |
| Collection of premiums at post-contract stage | No. | The mere collection of premiums from policyholders is unlikely, without more, to amount to assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance. |
| MID-TERM ADJUSTMENTS AND ASSIGNMENTS | ||
| Solicitors or licensed conveyancers discharging client instructions to assign contracts of insurance. | Not where article 67 applies. | As the assignment of rights under a contract of insurance (as opposed to the creation of new contracts of insurance) does not fall within the IMD, article 67 is of potential application (see PERG 5.11.9 G to PERG 5.11.12 G). |
| Making mid-term adjustments to a policy, for example, property manager notifies changes to the names of the leaseholders registered as "interested parties" in the policy in respect of the property. | Yes. | Assuming the freeholder (as policyholder) is obliged under the terms of the policy to notify the insurance undertaking of changes to the identity of the leaseholders, the property manager is likely to be assisting in the administration and the performance of the contract of insurance. |
| TRADED ENDOWMENT POLICIES ("TEPs") | ||
| Making introductions for the purposes of selling TEPs | Yes, unless article 72C applies. | Making introductions for these purposes is arranging unless article 72C applies (see PERG 5.6.5 G to PERG 5.6.9 G). The exclusions in article 29 (Arranging deals with or through authorised persons) and 33 (Introducing) no longer apply to arranging contracts of insurance. |
| Market makers in TEPs | Yes, although the exclusion in article 28 may apply. | Unauthorised market makers can continue to make use of the exclusions in articles 15 (Absence of holding out etc.) and 16 (Dealing in contractually based investments), where appropriate. In order to avoid the need for authorisation in respect of arranging they may be able to rely upon article 28 (see PERG 5.6.12 G). |
| ASSISTING POLICYHOLDER WITH MAKING A CLAIM | ||
| Merely providing information to the insured to help him complete a claim form | No. | Of itself, this is likely to amount to assisting in the administration but not the performance of a contract of insurance. In the FSA's view, the provision of information in these circumstances is more akin to facilitating performance of a contract of insurance rather than assisting in the performance (see PERG 5.7.3 G to PERG 5.7.5 G) |
| Completion of claim form on behalf of insured | Potentially. | This activity amounts to assisting in the administration of a contract of insurance. Whether this activity amounts to assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance will depend upon whether a person's assistance in filling in a claims form is material to whether performance of the contractual obligation to notify a claim takes place (see PERG 5.7.2 G to PERG 5.7.3 G). |
| Notification of claim to insurance undertaking and helping negotiate its settlement on the policyholder's behalf | Yes. | This activity amounts to assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance (see PERG 5.7.4 G). |
| ASSISTING INSURANCE UNDERTAKING WITH CLAIMS BY POLICYHOLDERS | ||
| Negotiation of settlement of claims on behalf of an insurance undertaking | No. | Claims management on behalf of an insurance undertaking does not amount to assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance by virtue of the exclusion in article 39B (see PERG 5.7.7 G). |
| Providing information to an insurance undertaking in connection with its investigation or assessment of a claim | No. | This activity does not amount to assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance. |
| Loss adjusters and claims management services (for example, by administration outsourcing providers) | Potentially. | These activities may amount to assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance. Article 39B excludes these activities, however, when undertaken on behalf of an insurance undertaking only (see PERG 5.7.7 G). |
| Providing an expert appraisal of a claim | No. | This activity does not amount to assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance whether carried out on behalf of an insurance undertaking or otherwise. |
| Jeweller repairs customer's jewellery pursuant to a policy which permits the jeweller to carry out repairs | No. | This activity does not amount to assisting in the administration and performance of a contract of insurance. It amounts to managing claims on behalf of an insurance undertaking and so falls within the exclusion in article 39B (see PERG 5.7.7 G). |
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15.5
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15.6
See Notes

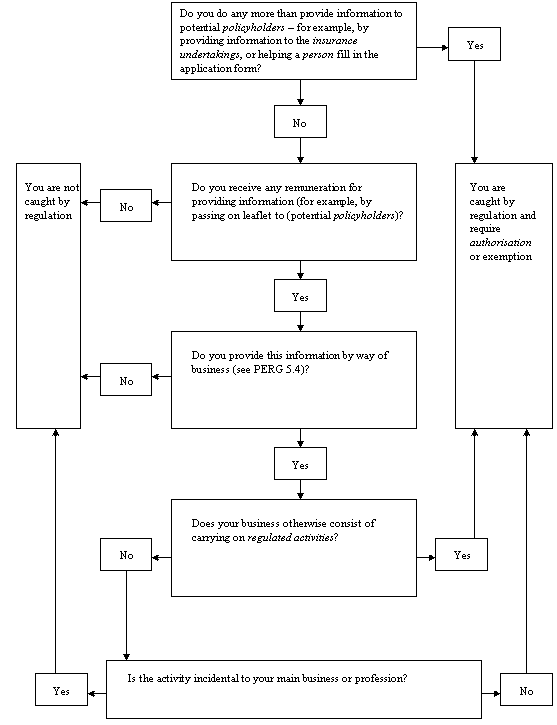
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15.7
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.15.8
See Notes

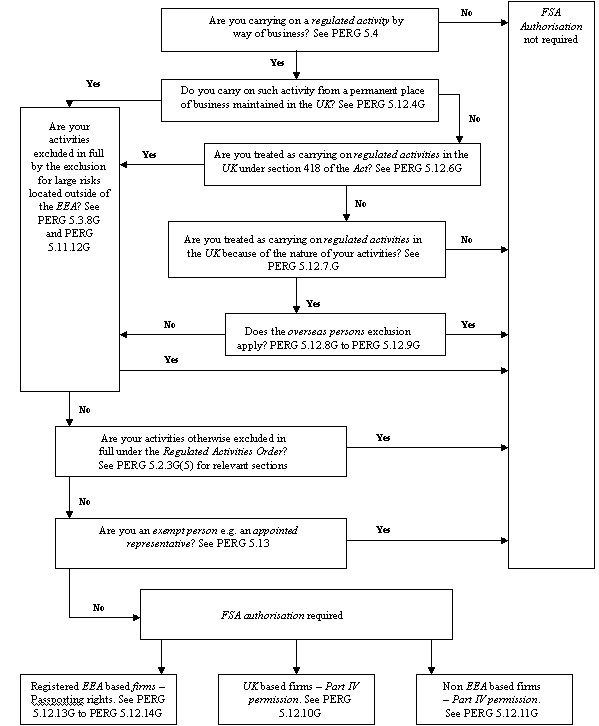
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.16
Meaning of 'insurance mediation'
- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.16.1
See Notes

- 01/07/2005
PERG 5.16.2
See Notes

"'Insurance mediation' means the activities of introducing, proposing or carrying out other work preparatory to the conclusion of contracts of insurance, or of concluding such contracts, or of assisting in the administration and performance of such contracts, in particular in the event of a claim.
These activities when undertaken by an insurance undertaking or an employee of an insurance undertaking who is acting under the responsibility of the insurance undertaking shall not be considered as insurance mediation.
The provision of information on an incidental basis in the context of another professional activity provided that the purpose of that activity is not to assist the customer in concluding or performing an insurance contract, the management of claims of an insurance undertaking on a professional basis, and loss adjusting and expert appraisal of claims shall also not be considered as insurance mediation."
- 01/07/2005
